Describe Two Ways Your Body Relies on the Cell Cycle
Click card to see definition. Regulation of cell cycle.
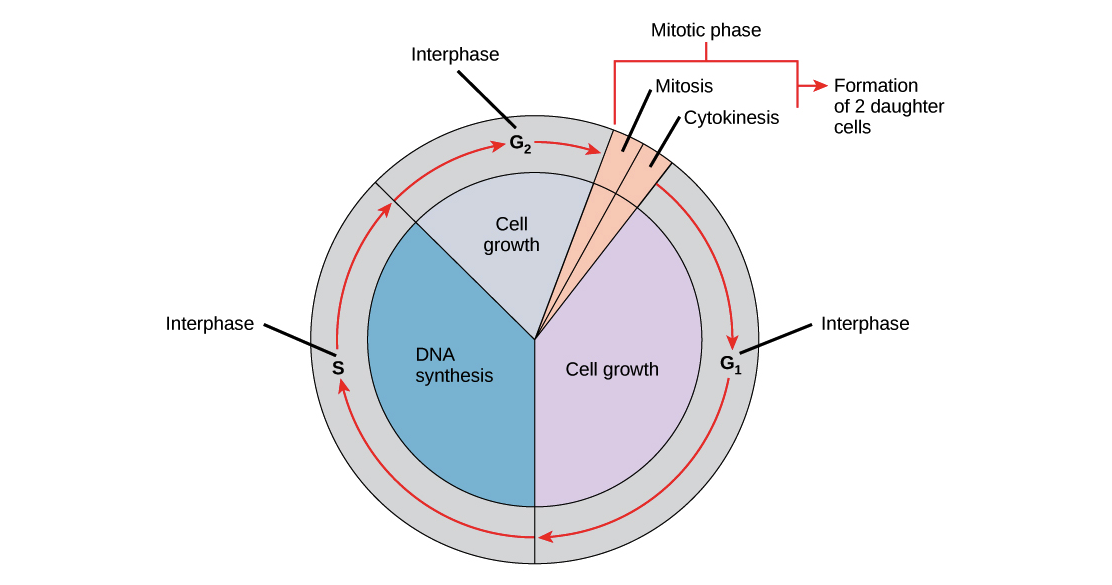
The Cell Cycle And Mitosis Review Article Khan Academy
Cell tissue organ organ system organism.
. Cell differentation begins with stem cells. The cell then leaves interphase undergoes mitosis and completes its division. Meiosis II halves the amount of genetic information in each chromosome of each cell.
Short term This type occurs within a relatively short period of time. Your body does not produce new brain cells. -Amino Acids are joined by peptide bonds to make polypeptides.
Explain how cell differentiation leads to the organization of a multicellular organism. Cancer the uncontrolled growth of cells often results in a tumor or mass of abnormal cells. Second internal regulation of the cell cycle is necessary to signal passage from one phase to the next.
A cell spends most of its time in what is called interphase and during this time it grows replicates its chromosomes and prepares for cell division. For eukaryotes consider an animal such as a cat if a cat. -Glucose molecules are combined to form glycogen.
Must include in your answer. -Acetyl CoA molecules are combined to make fatty acid chains. Multicellular- has more than one cell.
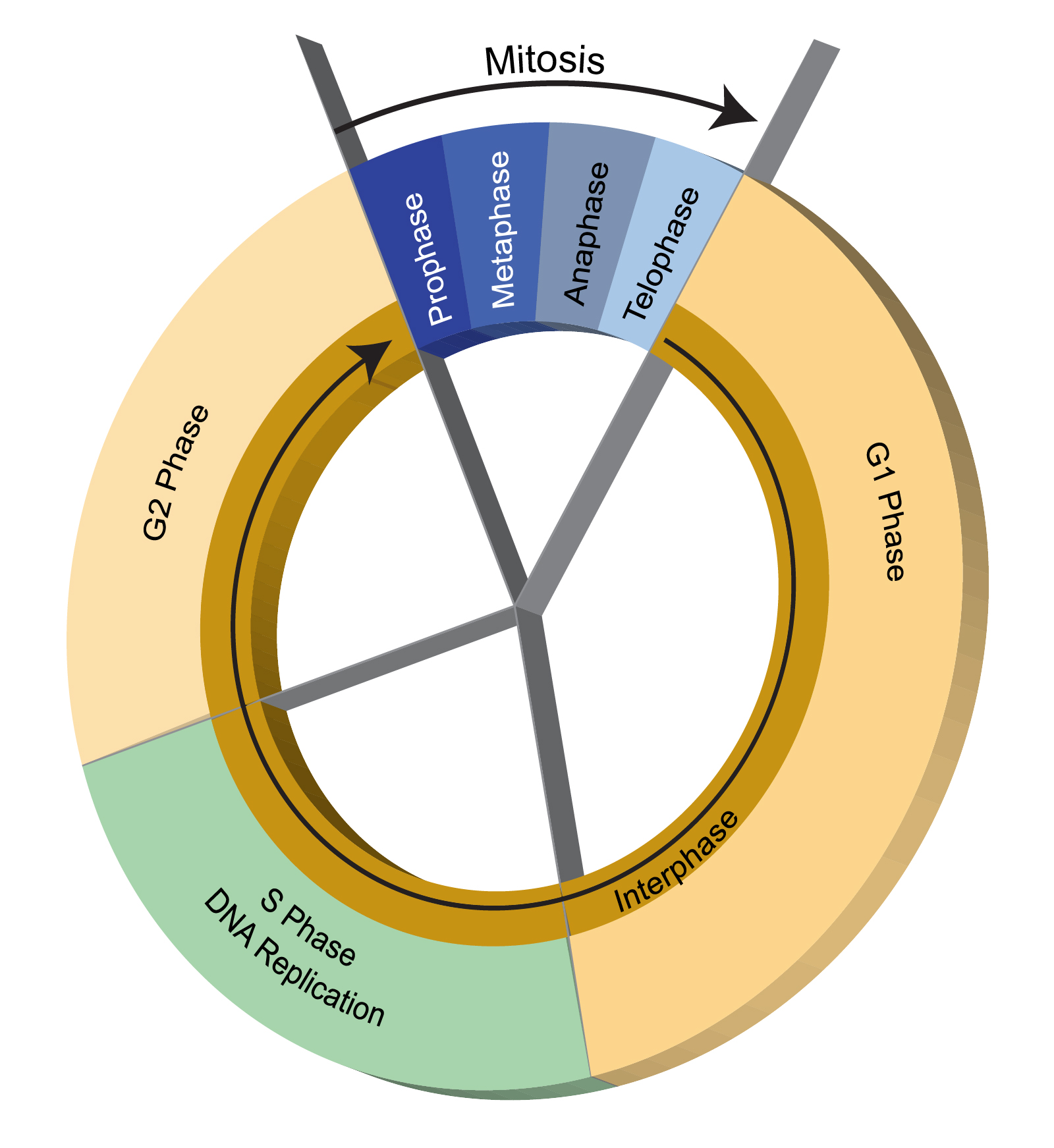
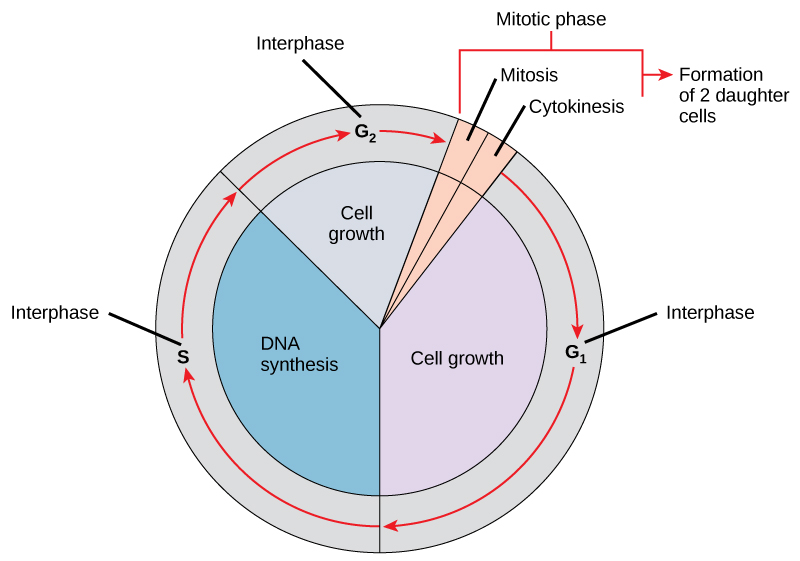
Interphase is the resting stage of a cell. The stages of the cell cycle in order are interphase prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase. Interphase and the mitotic M phase.
For prokaryotes the cell cycle called Binary Fission allows for them to live on by dividing into two new daughter cells. Growth factors cyclin CDKs. Unicellular- has one cell.
Use or absorb energy to combine simpler molecules into larger more complex ones. Through the cell cycle organisms grow develop repair old or damaged cells and produce new cells. The core control system of the cell cycle.
A typical eukaryotic cell cycle is divided into two main phases-Interphase. During M phase or mitosis the cell divides. Considering your answer to Questions 3 and 4 identify two ways that the growth of an organ-ism can be accomplished through the events of the cell cycle.
During one portion of interphase the cells DNA is copied. Human cells exhibit typical eukaryotic cell cycle and take around 24 hours to complete one cycle of growth and division. Long term This type takes thousands of years to occur.
Interphase is the time. During the mitotic M phase the cell separates its DNA into two sets and divides its cytoplasm forming two new cells. Chromosomes carry genetic information in a molecule called DNA.
Mar 5 2018. The two main divisions of the cell cycle are interphase and mitosis. 4 Daughter cells of mitosis have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell while daughter cells of meiosis have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
In this phase the cell increases in mass and organelle. Also known as the resting phase of the cell cycle. During this segment of the cell cycle a cell doubles its cytoplasm and synthesizes DNA.
Although it may sound counterintuitive one of the most direct ways to find out what a gene does is to see what happens to the organism when that gene is missing. It is important to organisms in different ways but overall it allows them to survive. It is estimated that a dividing cell spends about 90-95 percent of its time in this phase.
What are the two main ways that the cell cycle is controlled. Using a cell from your body as an example explain the stages in cell cycle. First if the cell cycle were not regulated cells could constantly undergo cell division.
The bacterial cell cycle involves the formation of new cells through the replication of DNA and partitioning of cellular components into two daughter cells. Carbon Cycle can be classified into two types based on the duration of the process into two types. If a cell that is in G1 is not biologically ready to continue on to S phase either because it has not reached a sufficient size or does not have the appropriate.
List these from smallest to largest ------organ organism organ system cell and tissue. Describe a process in the human body in which there is evidence of the cell cycle at work. During interphase the cell grows and makes a copy of its DNA.
The end result is four daughter cells called haploid cells. Tap card to see definition. A type of cell division called mitosis ensures that when a cell divides each.
This process is known as mitosis and is used to generate new cells. Two ways your body relies on the cell cycle. It is named as such because it takes just days months or years for carbon to flow across the various carbon reservoirs.
Stem cells have the ability to become any type of cell needed by the body. Meiosis has two cycles of cell division conveniently called Meiosis I and Meiosis II. The cell cycle is the replication and reproduction of cells whether in eukaryotes or prokaryotes.
3 Mention two differences between mitosis and meiosis. The two major phases of the cell cycle are interphase and M phase. In eukaryotic cells or cells with a nucleus the stages of the cell cycle are divided into two major phases.
This is the currently selected item. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. While this may be beneficial to certain cells on the whole constant reproduction without cause would be biologically wasteful.
Meiosis I halves the number of chromosomes and is also when crossing over happens. Cyclins cyclin-dependent kinases Cdks and the APCC. Control of the cell cycle is necessary for a couple of reasons.
Explain this observation using what you have. The duration of the cycle however varies from organism to organism and cell to cell. Cell organ organ system stem tissue.
The period prior to the synthesis of DNA.

Mitosis And Cell Cycle Taboo Game 32 Cards With Editable Template Taboo Game Cells Lesson Cell Theory

Cell Division Anatomy And Physiology

The Process Of Meiosis Boundless Biology Meiosis Biology Biology Notes

Types Of Cell Division Definition Mitosis Meiosis Binary Fission Meiosis Cell Division Cell

Interphase Definition And Stages Biology Dictionary

What Is Mitosis Biology 101 Free Biology Study Guides Mitosis Cell Division Meiosis

Mitosis Meiosis Mitosis Meiosis Mitosis Meiosis

Cell Cycle Genetic Engineering Info Cell Cycle Nobel Prize In Physiology Or Medicine Cell
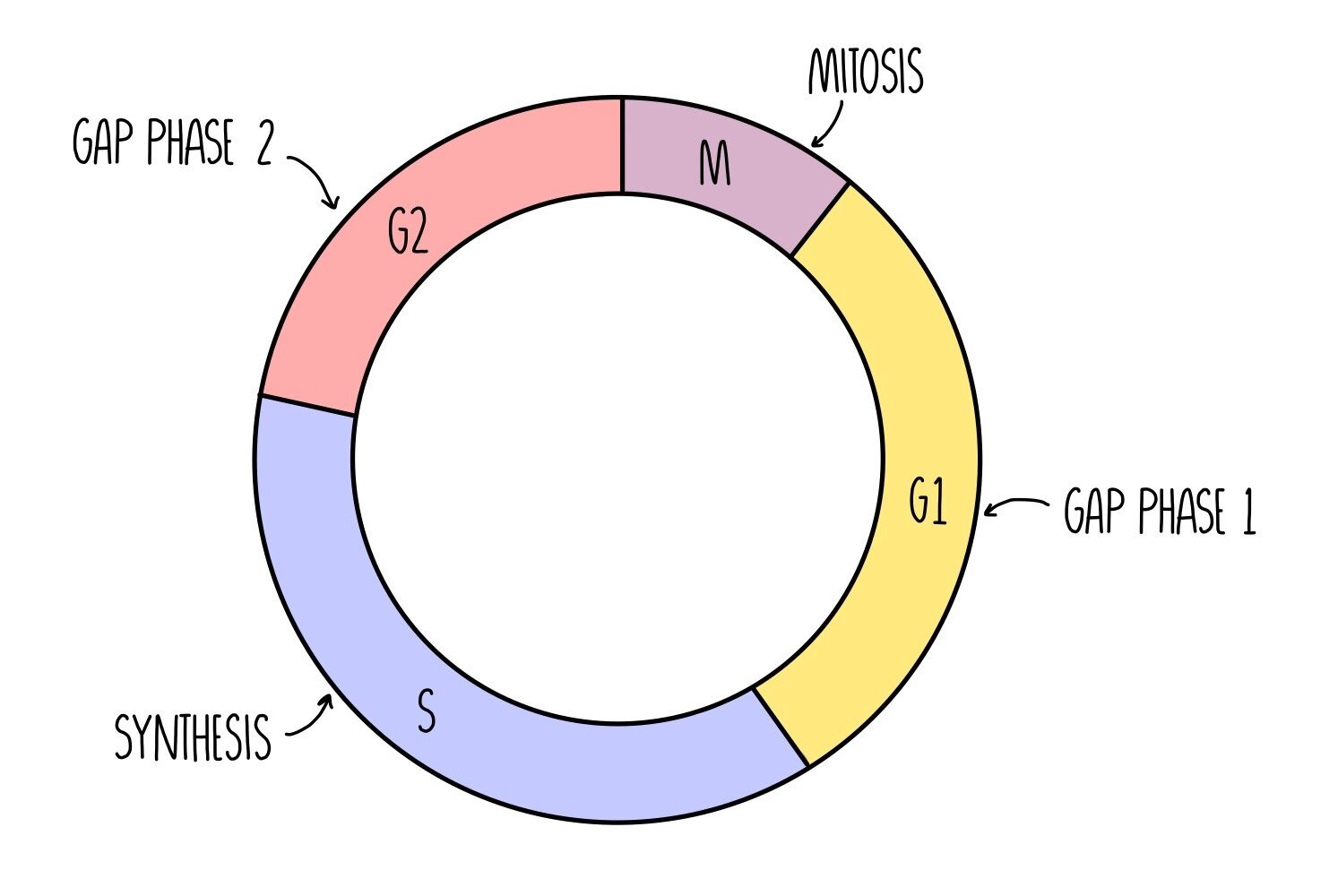
The Cell Cycle Mitosis Meiosis A Level The Science Hive

Somatic Cells Grow And Divide Via Mitotic Cell Cycle Or Stop Growing Become Arrested In Go Make Up The Vast Majority Of Mitosis Somatic Cell Cell Division
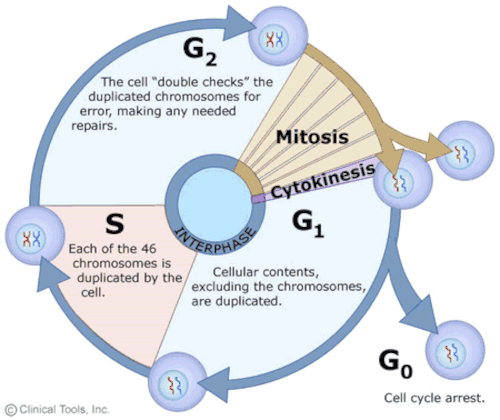
The Cell Cycle Mitosis And Meiosis For Schools And Colleges Virtual Genetics Education Centre University Of Leicester
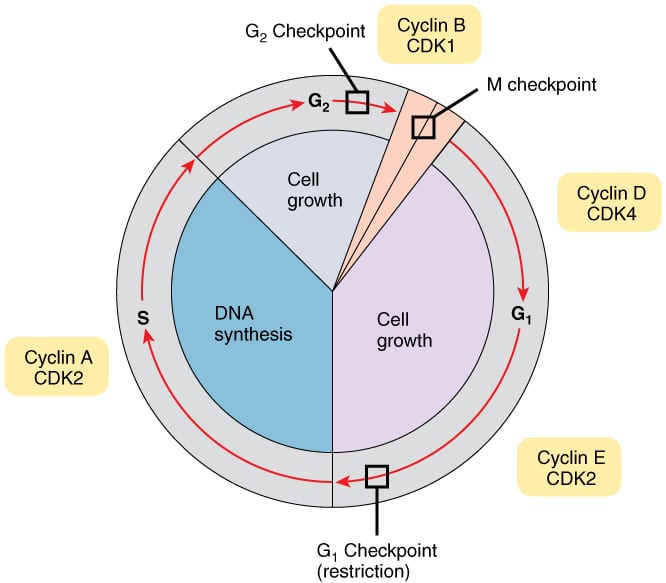
The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation Teachmephysiology

Control Of The Cell Cycle Biology I

The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation Teachmephysiology

Genetics Mitosis And Meiosis Meiosis Mitosis Cell Division

Throughout The Interphase Dna Remains In The Form Of Chromatin A Semi Condensed Form Of Dna During The S Phase An Identica Mitosis Cell Cycle Cell Division

Cell Cycle Regulation Cancer Genetics Cell Cycle Cell Biology
Comments
Post a Comment